Enhanced Pathways for Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Production
The production of Synthetic Paraffinic Kerosene (SPK), commonly referred to as
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), has advanced significantly. Numerous investments are
being made globally to establish SAF refineries to meet the growing demand driven by the
CORSIA initiative.
This initiative mandates blending traditional kerosene with SAF
to achieve critical climate action milestones.
Eurasia Industries and the Four Birds Impact Funds have considerable experience in sustainable development,
focusing on extractive natural resources, water reclamation, wetland protection.
They participate in the improvement of global value chains through technology and
organisational innovation. They have naturally entered this industry, providing
their experience to O&G and chemistry major companies to improve the SAF production
value chain by using state-of-the-art breakthrough technologies.
The HXELABS company is the result of these
cooperative endeavours and is actively
working to create new industrial pathways to improve this domain of industry.
Current SAF Production Technologies
Among the available pathways for SAF production,
Hydroprocessed Esters and Fatty Acids (HEFA) has emerged as a mature,
commercially viable technology, outperforming alternatives such as
Fischer-Tropsch, Alcohol-to-Jet, and Synthesized Iso-Paraffins.
The HEFA process hydrogenates fatty acids and lipid molecules
(mono-, di-, and tri-acylglycerols), coming from various feedstocks, including:
- Soybean oil
- Rapeseed oil
- Used Cooking Oil (UCO)
- Tallow and animal fats
- Vegetable oils from approved crops, such as Pongamia, Macauba, Camelina, Brassica carinata, and Jatropha.

Feedstock Challenges
The reliance on agricultural resources for feedstocks poses a significant
challenge to the SAF industry, as it must avoid competing with the food
supply chain. Despite efforts to rehabilitate non-arable
land and increase feedstock production through advanced agricultural
methods, sustaining long-term market demand will remain difficult.
Innovative Solutions by HXELABS and Partners
Long-Term Initiatives
HXELABS, in collaboration with OLILAB, is engaged in projects
such as Nordic Gardens and Desert Gardens. These initiatives
focus on developing high-yield crops and exploring innovative
solutions like algae and fungi cultivation. Although algae-based
biofuels were previously abandoned due to high costs and inefficient
oil extraction, HXELABS is adopting a novel approach, relying on wastewater
treatment within an Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture/Farming (IMTA/IMTF)
framework, and then applying enzymatic processes to break algae cell membranes
efficiently, releasing high-quality lipids and polysaccharides for both energy
and food applications.
This approach is not mature yet and R&D is still going on.
Short- to Medium-Term Focus
In the immediate term, HXELABS and HAIXIN are enhancing HEFA technology
by improving feedstock acceptance flexibility and process efficiency.
The combination of HAIXIN’s Mixed Cracking Treatment (MCT) and Suspended Bed Hydrogenation (SBH)
enables the treatment of diverse feedstocks, including solid agricultural residues.
This advanced pathway produces higher-quality SPK and achieves greater processing efficiency.
Accepted Feedstocks:
- UCO
- Animal fats
- Vegetable oils (e.g., soybean, rapeseed)
- Advanced crops (e.g., Pongamia, Camelina, Brassica carinata)
- Algae and halophytes
- Solid forestry and agricultural waste
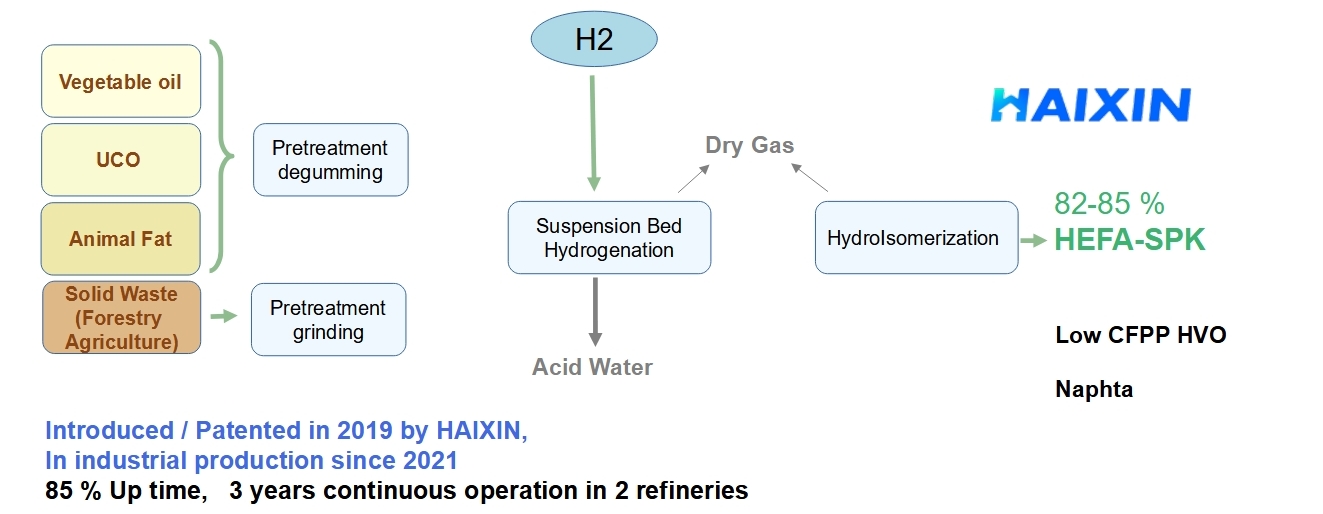
In a suspended bed system, the catalyst is in constant motion,
leading to better mixing of the vegetable oil feedstock with hydrogen.
This results in more efficient heat and mass transfer compared to fixed
bed systems, which is critical for the uniform hydrogenation and deoxygenation
of vegetable oils. The treatment of low-quality or acidic feedstocks is therefore
facilitated.
Suspended bed systems allow for continuous operation,
as the catalyst can be regenerated or replaced without
shutting down the reactor. This is particularly beneficial
in long-duration processes like SPK production, where maintaining
consistent output quality is essential. The ability to regenerate
the catalyst in situ without halting production reduces downtime and increases overall process efficiency.
Suspended bed catalysts are more tolerant to feedstock impurities,
which are common in vegetable oils, including metal and phophorus content.
This tolerance reduces the risk of catalyst deactivation, leading to a longer
catalyst life and more stable operation.
Characteristics
- Flash point: 45 °C
- Freeze point: -47 °C
- Energy Density: 43.9 MJ/KG
- Thermal stability: Excellent
- GHG Reduction: Up to 85% compared to petroleum-derived fuels
- Compatibility: Fully compatible with current aircraft technology and jet fuel specifications
Certifications and Standards
- ASTM D7566 Annex 2 (aviation turbine fuel)
- ISCC CORSIA
Environmental and ESG impact :
The CORSIA LCA methodology provides a complete and accurate assessment of
carbon dioxide savings along the value chain.
A wider acceptance of feedstock will bring additional
opportunities along the value chain.
The Multi Cracking treatment process allows to use up to 30% of solid waste
containing polysaccharides into the reactor. These solid wastes offer new commercial
opportunities to the agricultural sector through the processing of agricultural wastes rich in
cellulose, nut shells and even new crops, contributing to the economic development of rural areas
and offering the possibility of new activities on existing farmland, but also on new territories
where the exploitation of lower quality crops and vegetation is possible (forestry wastes, etc.).
More information :
HX ENERGY LABS.









